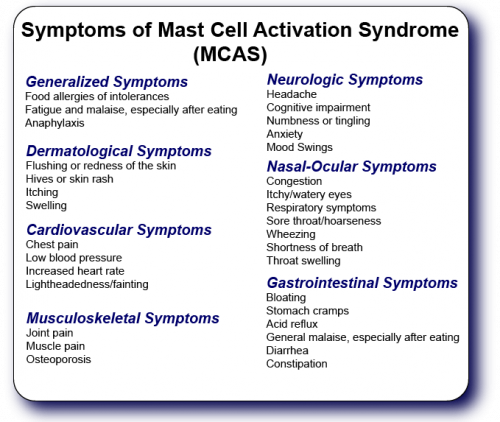
Mast cell stabilisers, leukotriene antagonists and antihistamines: A rapid review of the evidence for their use in COVID-19 - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine

Mast cell inhibitors. Various classes of mast cell inhibitors already... | Download Scientific Diagram

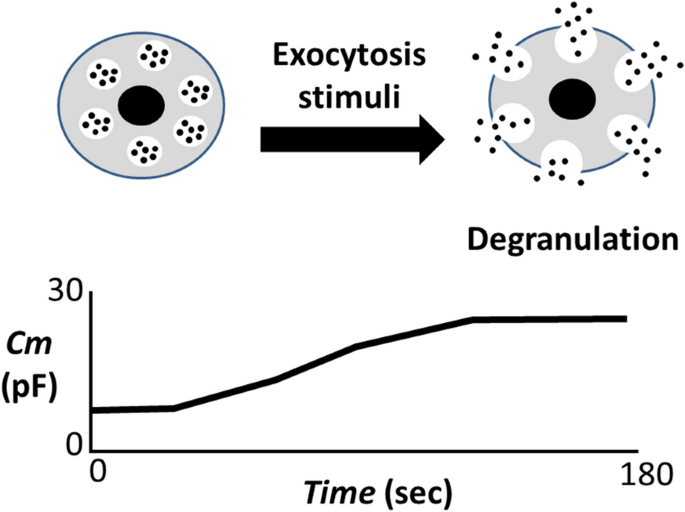
Effects of anti-allergic drugs on exocytosis-induced membrane surface... | Download Scientific Diagram
Potential prophylactic efficacy of mast cell stabilizers against COVID-19 vaccine-induced anaphylaxis | Clinical and Molecular Allergy | Full Text

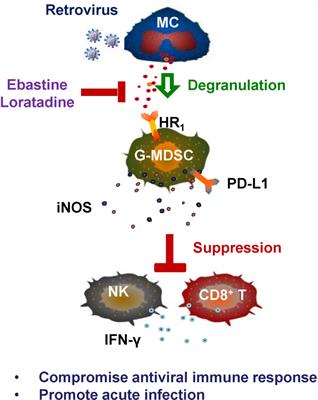
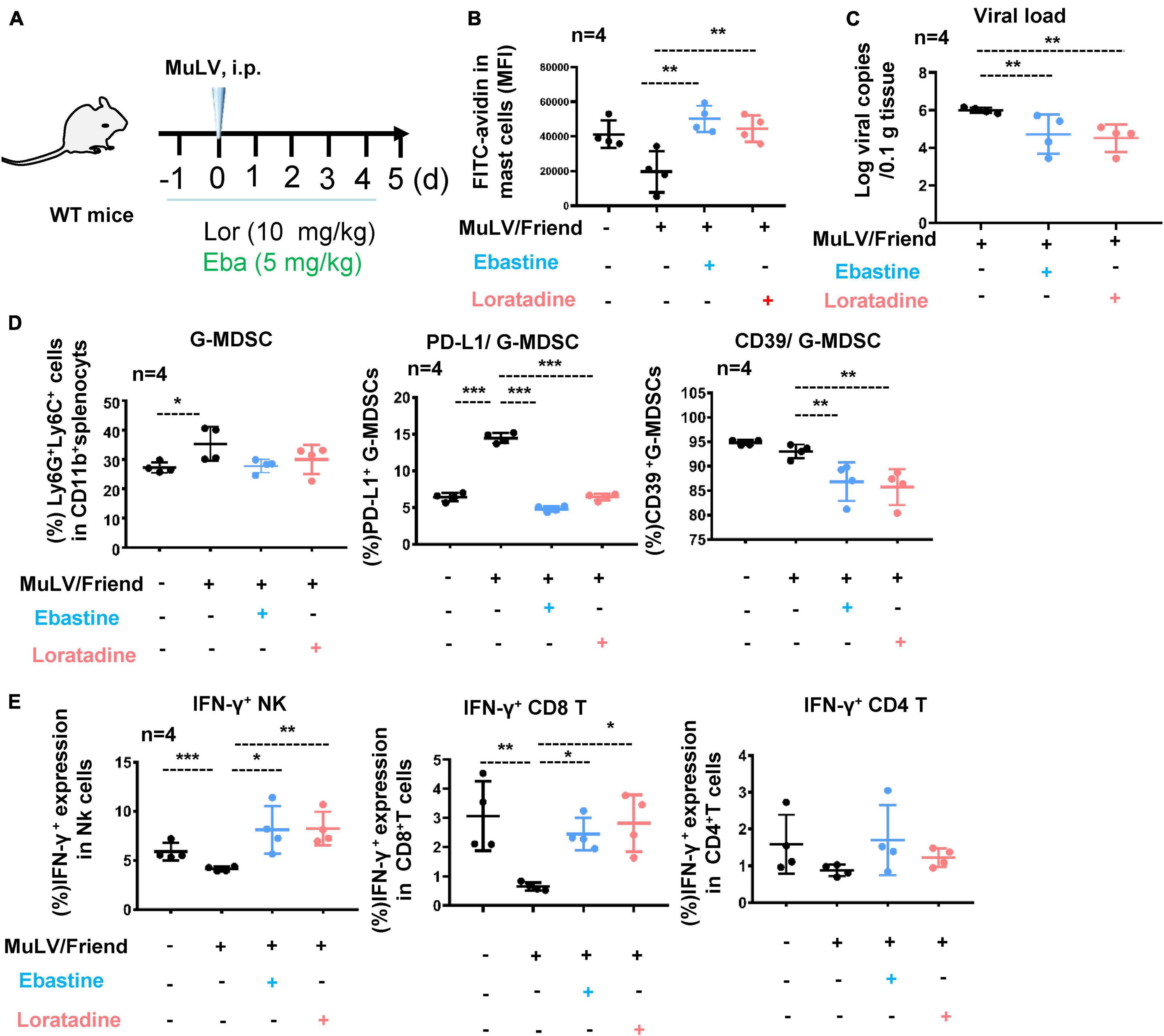
Loratadine, an antihistamine drug, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through suppression of the NF-kB pathway - ScienceDirect

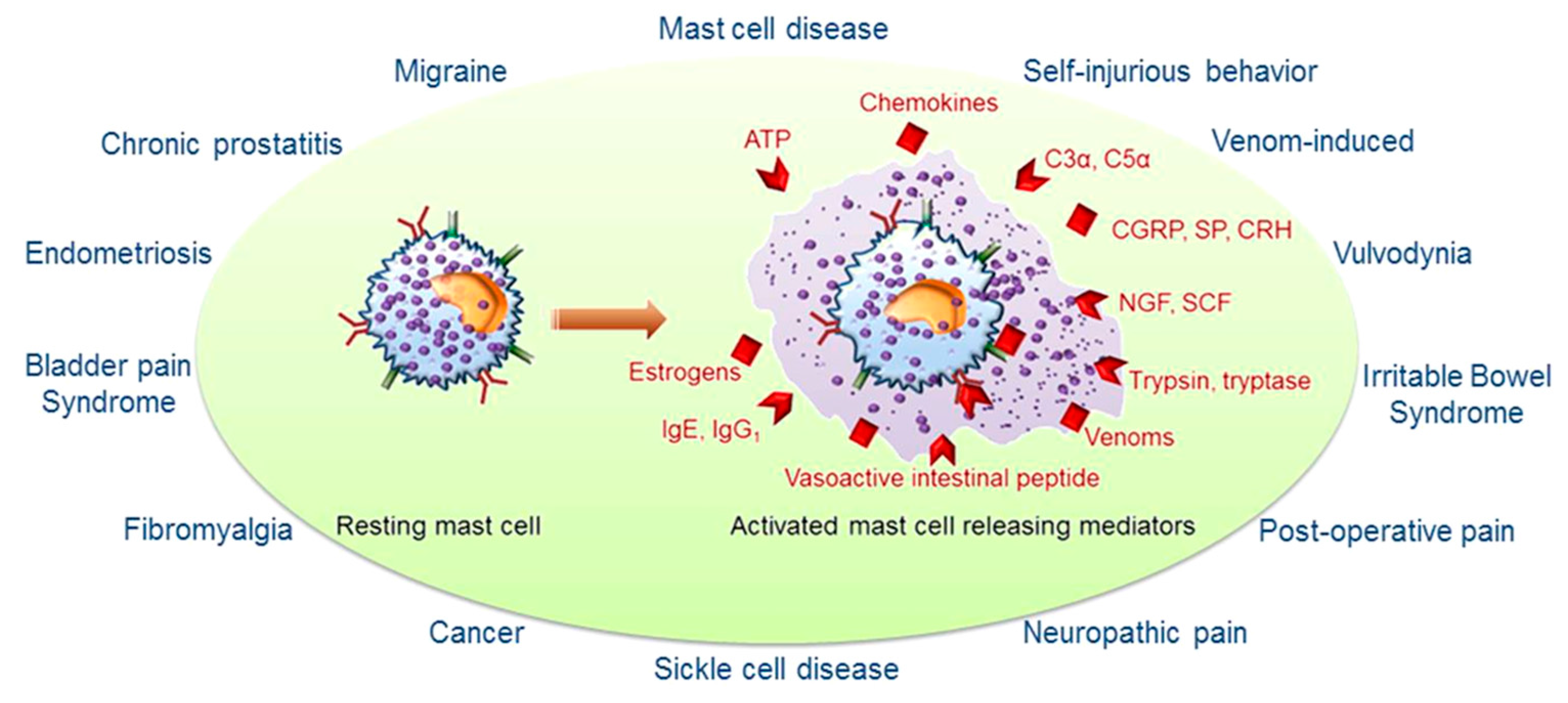
Mast cells: Therapeutic targets for COVID‐19 and beyond - Lam - 2021 - IUBMB Life - Wiley Online Library

Potential prophylactic efficacy of mast cell stabilizers against COVID-19 vaccine-induced anaphylaxis | Clinical and Molecular Allergy | Full Text
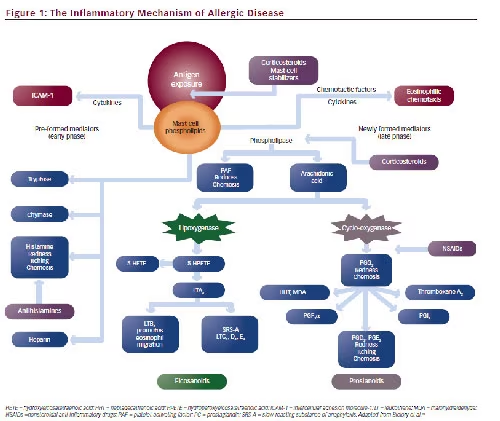
Topical Corticosteroids and Antihistamines—Mast Cell Stabilizers for the Treatment of Allergic Conjunctivitis - touchOPHTHALMOLOGY